
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded in 1945. UN currently has 193 Member Countries. The purposes and principles while founding the UN drive its work and vision now. The main goal of the UN is to maintain international peace and security, form friendly relations among nations, reach international associations, and be a center for coordinating the activities of countries.

The UN can be known as one place where the world's nations can assemble, consult common concerns, and find shared solutions. United Nations adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, in 2015. It acts as a versatile call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity. The UN developed 17 Sustainable Development Goals and aims to achieve them by 2030. Each goal has 8–12 targets, and each target has between one and four indicators used to measure progress toward attaining the end goal. The 17 goals are combined—they realize that activity in one area will affect outcomes in others and that growth must balance social, economic, and environmental sustainability. Countries have dedicated to prioritizing progress for those who are furthest behind. The SDGs aim to end poverty, hunger, AIDS, and discrimination against women and girls. The creativity, know-how, technology, and financial resources from humankind are essential to achieve the SDGs in every context. The 17 goals include poverty, education, health, hunger, clean energy, equality, and more.
You may hear the word sustainability everywhere now. But what does that even mean?

Sustainability means fulfilling the needs of current generations without compromising the needs of future generations while guaranteeing harmony between economic growth, environmental care, and social well-being. Having noted this factor, the UN framed the sustainability goals to enhance this earth for a better future.
The UN has formed 17 Sustainability Development Goals, and the 2nd goal is Zero Hunger. The main target of this goal is to end all forms of hunger and malnutrition by 2030. It confirms that all people–especially children–have sufficient and nutritious food all year.

The aim of this goal is to put an end to hunger, attain food security, improve nutrition, and encourage sustainable agriculture. This goal also involves promoting sustainable agriculture, supporting small-scale farmers and access to land equally, technology and markets. Improving agricultural productivity necessitates international cooperation for investing in infrastructure and technology
The growth of a sustainable environment gets obstacles due to extreme hunger and malnutrition. People cannot easily escape from this unfortunate situation. People with hunger and malnutrition are less productive. They are more prone to disease and unable to earn more and improve their livelihoods.

It is concerning that two billion individuals lack consistent access to safe, nutritious, and adequate food. In the year 2019, 144 million children under the age of five were stunted, while 47 million children were impacted by wasting.
Over the last two decades, the number of undernourished individuals has seen a significant decrease of almost 50% due to the rapid economic growth and enhanced agricultural productivity.
In 2019, over 690 million individuals did not have access to basic food, primarily in Asia and Africa. Due to financial or resource-related constraints, folks experiencing moderate food insecurity face challenges in consuming a healthy and balanced diet regularly. Unless there are significant changes, it is estimated that around 840 million individuals will face hunger by 2030. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to worsen the situation even further.
In addition to the prevailing famine and hunger crisis, the pandemic poses an additional threat to food systems. Civil insecurity and declining food production trigger food scarcity and high food costs.
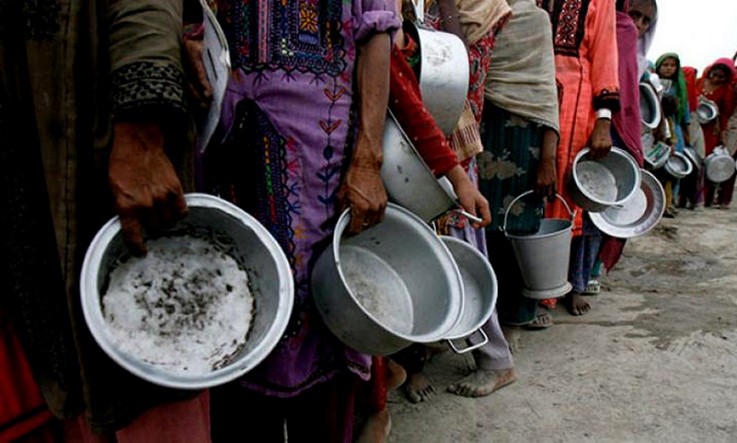

The agriculture sector must be nurtured by investing large amounts here. It is most required to reduce hunger and poverty, improve food security, create employment, and build resilience to disasters and shocks.

UN has set targets to achieve this goal by 2030. The targets include,

Food insecurity is defined by the UN FAO as the "situation when people lack access to sufficient amounts of safe and nutritious food for normal growth and development and an active and healthy life." The UN's FAO uses the prevalence of undernourishment as the hunger indicator.
The FAO took inspiration from various pioneering countries in this field and extended their systems to a global level. The "Food Insecurity Experience Scale" (FIES) survey module comprises eight questions that were chosen and tested thoughtfully and have been proven to be effective in evaluating the severity of food insecurity in diverse cultural, linguistic, and developmental contexts.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused economic shocks that resulted in 83 to 132 million people experiencing food insecurity in 2020.
It has two indicators,
his target has one indicator,
It has two Indicators
Biodiversity is key to food security and nutrition and ensures sustainable increases in agricultural production. The rapid increase in environmental and social changes is causing threats to the diversity of both plant and animal genetic resources.
Unlike most SDGs that have a target date of 2030, this goal is set for the year 2020.
The plan involves
It has two indicators,
The "Agriculture Orientation Index" (AOI) measures government support for agriculture by comparing spending to the sector's contribution to the economy. AOI > 1 indicates more spending, while AOI < 1 indicates less focus on agriculture.
Target 2.b. has two indicators,
This target has one indicator,
These are the various targets and their indicators of the SDG-2 Zero Hunger.
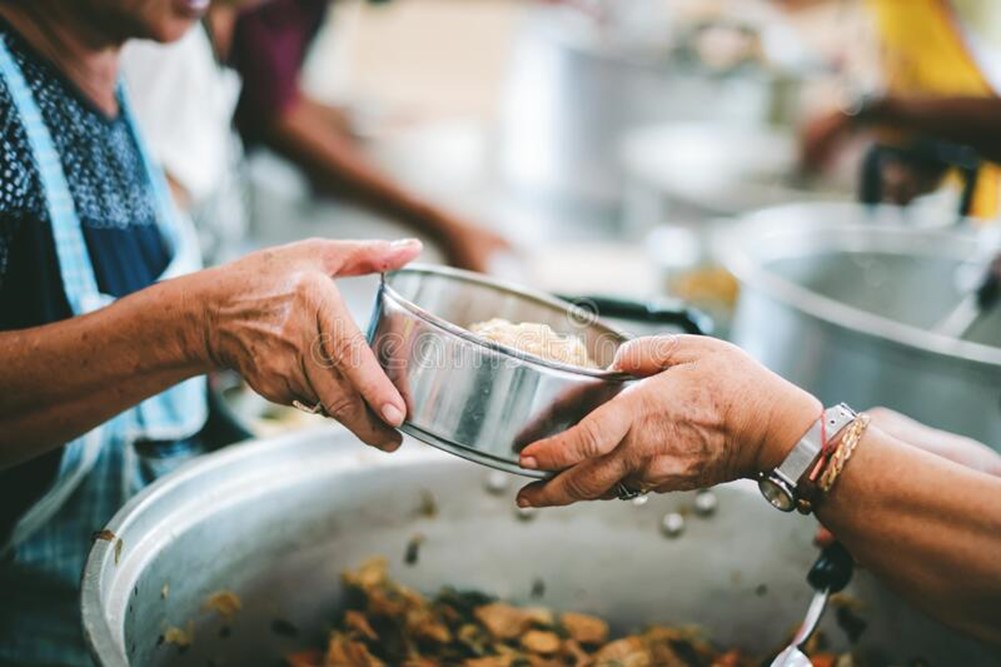

Access to safe and nutritious food for our families is a universal desire. A world without hunger can significantly impact our economies, education, health, equality, and social development, making it crucial for building a better future for all. It's worth noting that hunger can hinder human development, making it difficult to achieve other sustainable development goals such as education, health, and gender equality.
To ensure food security, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This includes implementing social protection programs to ensure safe and nutritious food is available, particularly for children. Additionally, transforming our food systems is crucial to creating a more sustainable and inclusive world.
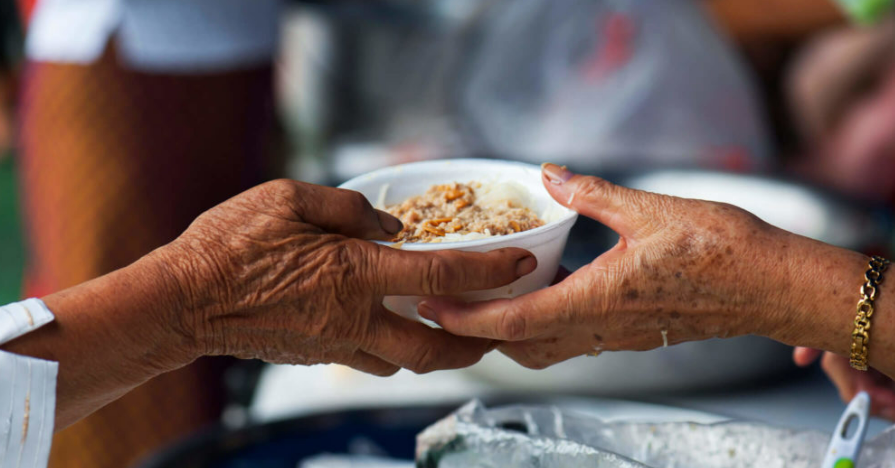

Investing in both rural and urban areas to provide social protection is necessary to ensure that impoverished individuals have access to food and can improve their livelihoods.

Supporting local farmers and markets is an effective way to make positive changes in your life, home, workplace, and community. By making sustainable food choices, promoting good nutrition, and reducing food waste, you can contribute to the goal of achieving Zero Hunger. As a consumer and voter, you have the power to demand that businesses and governments prioritize this cause. Join the conversation either on social media platforms or in your local communities to make a difference. By acting on the above points, you can bring your commitment to achieving the goal by 2030. By acting on the above points, you can bring your commitment to achieving the goal by 2030.